Glen Report 6.15: New Labeling Reagents
Cholesterol, 2,4-dinitrophenol and psoralen had nothing whatsoever in common - until now. CE phosphoramidites containing these molecules are now available and their diverse purposes are briefly discussed below.
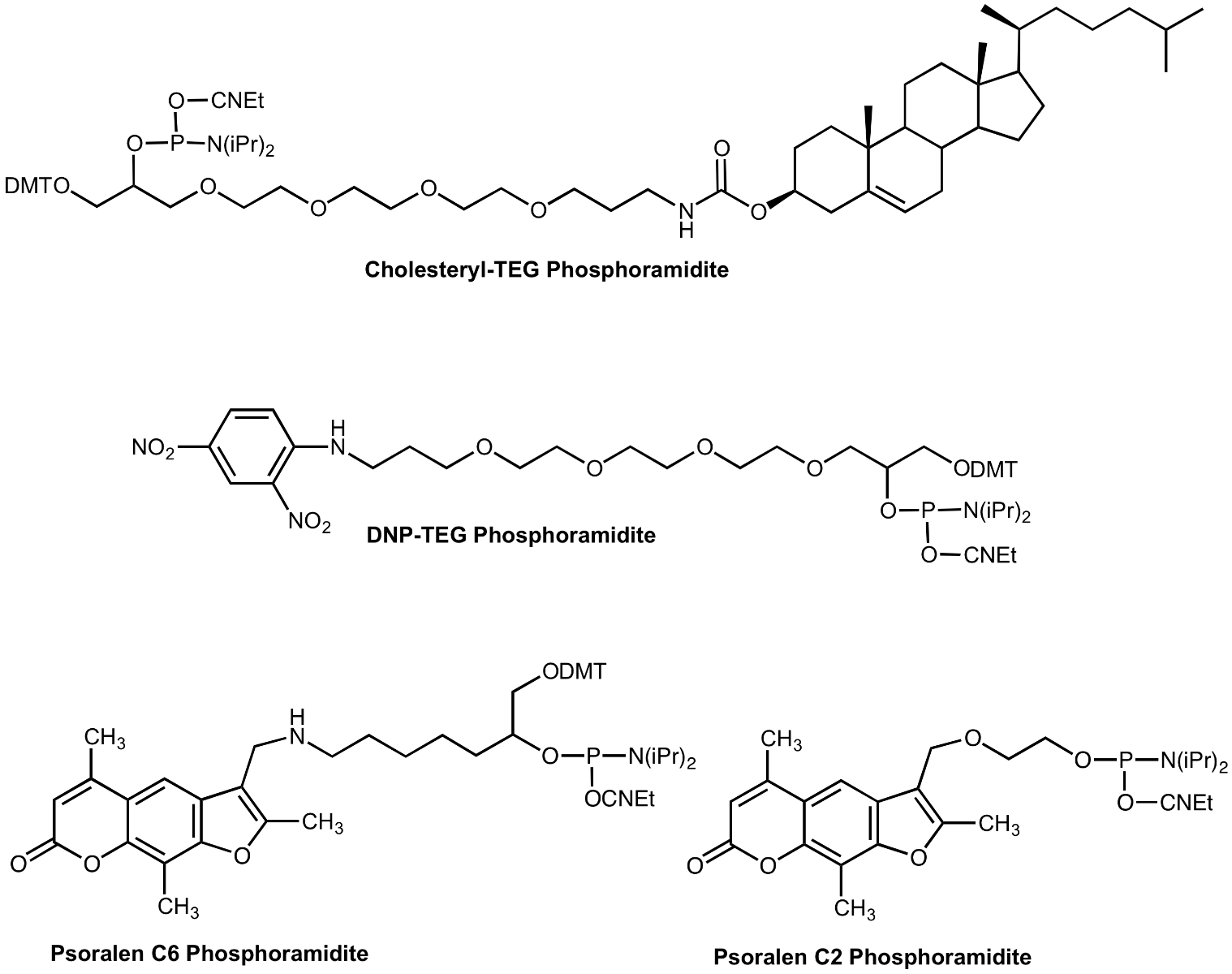
Cholesteryl-TEG Phosphoramidite
Potential therapeutic oligonucleotides must permeate the cell membrane for optimal activity. The addition of lipophilic groups to an oligonucleotide would be expected to enhance activity. The use of cholesteryl oligos and the consequent improvement in activity has been described1,2. We have designed our Cholesteryl Phosphoramidite with our branched triethyleneglycol (TEG) spacer for maximum solubility in acetonitrile as well as for applications requiring multiple labels.
DNP-TEG Phosphoramidite
A new analytical test based on detection of 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) labelled oligonucleotides with anti-DNP antibodies has been proposed3. Again, we have chosen the branched TEG spacer in our version of DNP phosphoramidite since it can be added once or several times to the 3' or 5' terminus.
Psoralen C2 and C6 Phosphoramidites
The use of Psoralen C2 Phosphoramidite for addition to the 5' terminus and to serve as an intercallating and cross-linking reagent in double-stranded oligonucleotides has been described4. This reagent has proved to be both successful and popular. However, to complement current psoralen C2 labelling, it is necessary to add to our product line a further psoralen phosphoramidite with a 6 atom spacer arm. In this way, the psoralen molecule can intercallate and cross-link with a triplex oligonucleotide strand5. We are, therefore, happy to introduce the Psoralen C6 Phosphoramidite which can be added to the 5' terminus and indeed to specific locations within the sequence. The utility of psoralen labelling has been demonstrated in several recent6,7,8,9 publications.
References
(1) C. Mackellar, D. Graham, D.W. Will, S. Burgess, and T. Brown, Nucleic Acids Res., 1992, 20, 3411-3417.
(2) C.A. Stein, R. Pal, A.L. Devico, G. Hoke, S. Mumbauer, O. Kinstler, M.G. Sarngadharan, and R.L. Letsinger, Biochemistry, 1991, 30, 2439-2444.
(3) D.W. Will, C.E. Pritchard, and T. Brown, Carbohydrate Research, 1991, 216, 315-322.
(4) U. Pieles and U. Englisch, Nucleic Acids Res., 1989, 17, 285.
(5) M. Takasugi, A. Guendouz, M. Chassignol, J.L. Decout, J. Lhomme, N.T. Thuong, and C. Helene, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1991, 88, 5602-5606.
(7) O. Gia, S.M. Magno, A. Garbesi, F.P. Colonna, and M. Palumbo, Biochemistry, 1992, 31, 11818-11822.
(8) C. Giovannangeli, N.T. Thuong, and C. Helene, Nucleic Acids Res., 1992, 20, 4275-4281.
(9) C. Giovannangeli, M. Rougee, T. Garestier, N.T. Thuong, and C. Helene, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1992, 89, 8631-8635.
Product Information
Cholesterol Labelling
DNP Labelling
Psoralen Labelling
- Glen Report 6.11: Post-Synthesis Substitution - Convertible Nucleosides
- Glen Report 6.12: 2'-OMe-RNA Update
- Glen Report 6.13: DeoxyUridine Derivatives for Internal Modification
- Glen Report 6.14: 5' To 3' Synthesis
- Glen Report 6.15: New Labeling Reagents
- Glen Report 6.16: Etheno-dA and Etheno-A - Fluorescent Monomers