Glen Report 6.16: Etheno-dA and Etheno-A - Fluorescent Monomers
Fluorescent derivatives are produced by reaction of chloroacetaldehyde with adenosine forming the corresponding 1,N6-etheno compounds. The resulting extension of conjugation allows specific excitation of etheno-A residues in the presence of protein fluorescence (1).
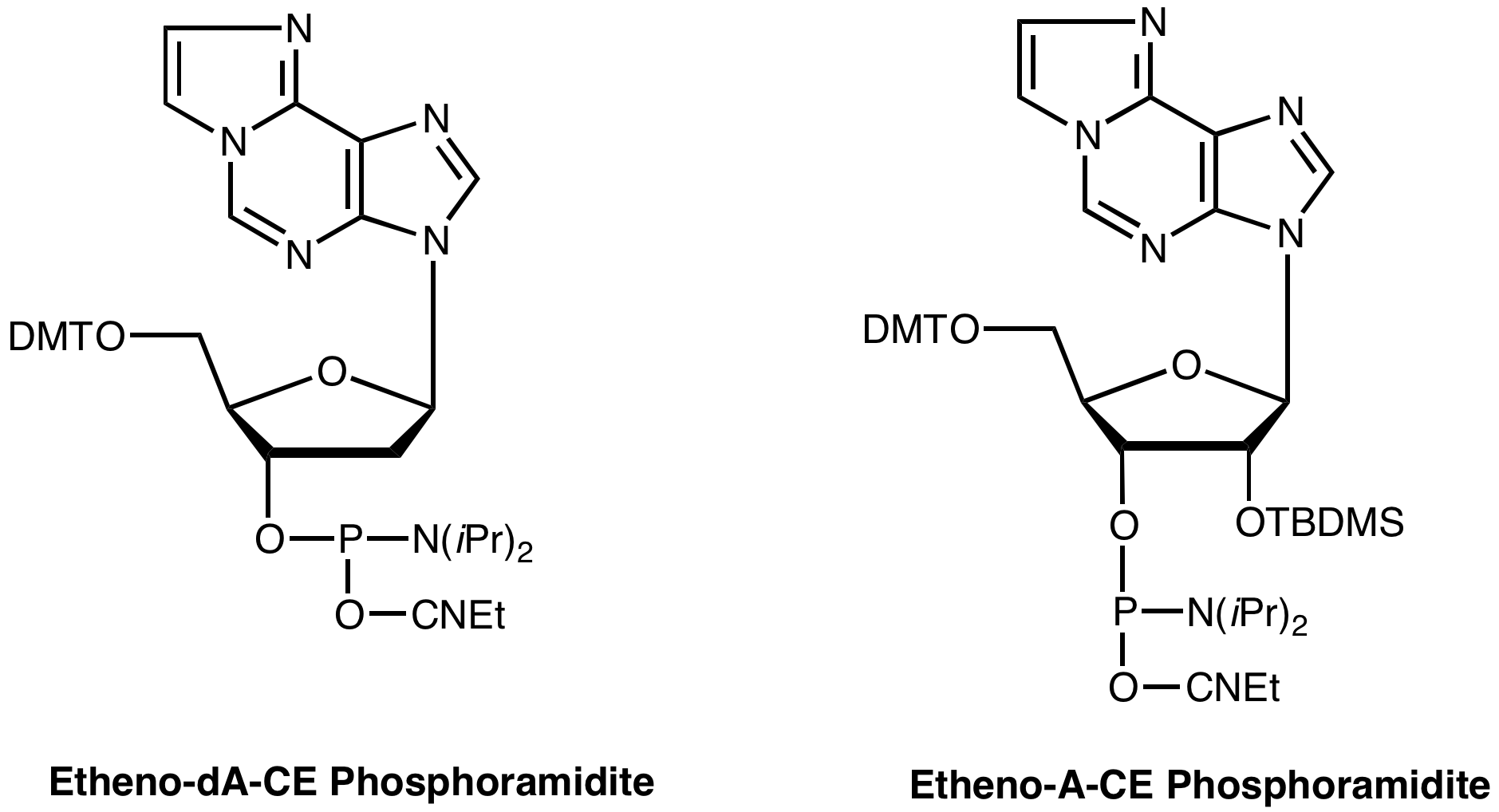
The availability of the CE phosphoramidite of etheno-dA allows the residue to be specifically located within sequences of interest. Applications may be found in carcinogenosis studies as well as in studies of DNA and RNA structures.
Etheno-dA residue is base sensitive and mild procedures should be employed for deprotection of the derived oligonucleotides. We recommend deprotection with ammonium hydroxide for 24hr at room temperature.
Reference
J.A. Secrist, J.R. Barrio, N.J. Leonard, and G. Weber, Biochemistry, 1972, 11,3499-3506.
Product Information
Etheno-dA-CE Phosphoramidite (10-1006)
Etheno-A-CE Phosphoramidite(10-3006) has been discontinued
- Glen Report 6.11: Post-Synthesis Substitution - Convertible Nucleosides
- Glen Report 6.12: 2'-OMe-RNA Update
- Glen Report 6.13: DeoxyUridine Derivatives for Internal Modification
- Glen Report 6.14: 5' To 3' Synthesis
- Glen Report 6.15: New Labeling Reagents
- Glen Report 6.16: Etheno-dA and Etheno-A - Fluorescent Monomers