Glen Report 22.16:; New Products – α-Tocopherol-TEG Phosphoramidite and 3'-Thiol-Modifier 6 S-S CPG
α-Tocopherol-TEG Phosphoramidite
One of the fastest growing segments of the Glen Research product line is our cholesteryl products for adding a lipophilic molecule to oligonucleotides. Cholesteryl modification of oligonucleotides, usually antisense or siRNA, allows them to be delivered more efficiently to the targeted cells. Cholesterol is a very “sticky” molecule with some inherent problems for oligonucleotide synthesis, purification, and transport in biological fluids. Cholesterol is also routinely isolated from animal sources and, as such, is not ideal for therapeutic development. Purely synthetic cholesterol is now available commercially but at a high cost.
Vitamins would be considered to be virtually the ideal carriers for therapeutic oligonucleotides since they are recognized and used by target cells but are not produced by these cells. Vitamin E is both lipophilic and non-toxic even at high doses so would be an excellent candidate as a lipophilic carrier for oligonucleotides. Therefore, as an addition to our cholesteryl product line, we would like to offer simple α-tocopheryl labelling. a-Tocopherol is better known as Vitamin E. Even though vitamin E is generally isolated from plant sources, totally synthetic a-tocopherol is commercially available and is racemic at its three chiral centers.
The use of a-tocopherol as a lipophilic carrier for ribozymes has been described.1 In this publication, a 5'-DL-α-tocopheryl phosphoramidite was used as a lipophilic capture tag with a cleavable linker as a tool for the purification of modified hammerhead ribozymes. In a more recent report,2 a-tocopherol was used as a lipophilic carrier for siRNA for efficient delivery to the liver. In this work, the phosphoramidite was prepared by simple phosphitylation of α-tocopherol.
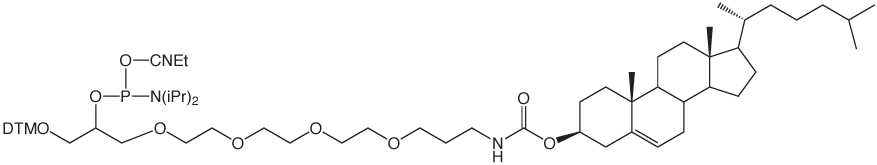
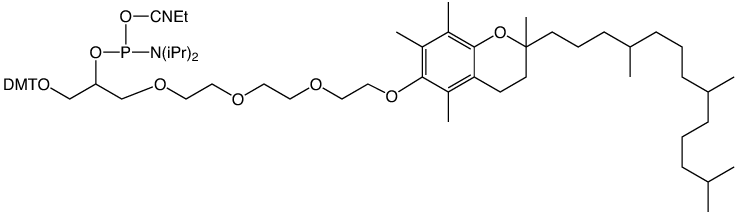
Over the years, we have developed a clear preference for the use of ethyleneglycol spacers for separating tags from oligonucleotides. These mixed polarity spacers allow the tag to be readily detected without interfering with oligonucleotide function. We are therefore happy to introduce a-Tocopherol-TEG Phosphoramidite for simple labelling of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. α-tocopheryl oligonucleotides can be deprotected using standard procedures.
References
- B.S. Sproat, T. Rupp, N. Menhardt, D. Keane, and B. Beijer, Nucleic Acids Res., 1999, 27, 1950-1955.
- K. Nishina, et al., Mol Ther, 2008, 16, 734-40.
Product Information
α-Tocopherol-TEG Phosphoramidite (10-1977)
3'-Thiol-Modifier 6 S-S CPG

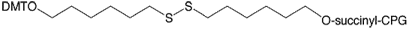

During 2008, Glen Research introduced 3'-Thiol-Modifier C6 S-S CPG (20-2936) to supplement the C3 version (20-2933) and the Thiol-Modifier C6 S-S Phosphoramidite (10-1936), which can easily and efficiently be used to produce 3'-thiols. This seemed like an easy addition to our product line but the reality was quite different. Many batches of 3'-Thiol-Modifier C6 S-S CPG have been produced and rejected for a variety of performance reasons. Even batches that have met our quality criteria failed to perform as well as the C3 version. We suspect that the C6 linker is too hydrophobic to perform at the highest level. Our colleagues at have come up with a simple change to the structure of this linker that has had a huge impact on performance. The substitution of an O for CH2 in the linker has elevated the performance of this new version (20-2938) to the highest level that we would expect. We are pleased to offer this product as a direct replacement for 3'-Thiol-Modifier C6 S-S CPG (20-2936).
3'-Thiol-Modifier C6 S-S CPG was developed by, and is sold under agreement from .
Product Information
- Glen Report 22.11: Simple Oligonucleotide Modification using Click Chemistry
- Glen Report 22.12: The copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC)
- Glen Report 22.13: tC, tCo and tCnitro: Tricyclic Cytosine Probes of DNA and RNA Structure
- Glen Report 22.14: Saccharin 1-Methylimidazole - An Activator for DNA and RNA Synthesis
- Glen Report 22.15: New Product - A dG Amino-Modifier with Improved Hybridization Characteristics
- Glen Report 22.16:; New Products – α-Tocopherol-TEG Phosphoramidite and 3'-Thiol-Modifier 6 S-S CPG
- Glen Report 22.17: New Products - 8-Oxo-G Clamp and 5'-Amino-Modifier TEG CE Phosphoramidites
- Glen Report 22.18: Deprotection – Volume 4 – Alternatives to Ammonium Hydroxide
- Glen Report 22.19: Technical Brief - Depurination
- Glen Report 22.110: Glen-Pak™ Product Update: New Protocols for Desalting and Purification