Glen Report 22.110: Glen-Pak™ Product Update: New Protocols for Desalting and Purification
We continue to develop new protocols for our popular Glen-Pak™ product line. While DMT-ON purification is the Glen-Pak's obvious strength, our Technical Support team routinely receives questions about other applications using the cartridges.
In this article, we introduce protocols for desalting of crude, DMT-Off DNA and RNA, DMT-ON purification of phosphorothioate oligos, as well as a method for purification of 5' labelled Cy5 and Cy5.5 oligos to separate them from their degradation products created during base deprotection requiring ammonium hydroxide.
Step by step versions of these new protocols can be viewed in our latest update of the Glen-Pak User Guide found in the purification section of our website or by following this URL: User Guide to Glen-Pak™ Purification
Desalting of DNA and RNA on the Glen-Pak DNA cartridge:
One of the most common questions we have received since the launch of Glen-Pak cartridges is whether or not they can be used for simple desalting of DMT-Off oligos. While our original protocol in this area was less than ideal and the more recent version of our Glen-Pak User Guide only offered options for desalting of DNA post PAGE or HPLC purification, we are now pleased to offer protocols for the desalting of DMT-Off DNA and RNA. Of special note is that the methods use the Glen-Pak DNA cartridge for desalting of BOTH types of oligos. This will allow our customers currently using more than one cartridge platform for downstream processing to harmonize to only one column type for both DNA and RNA DMT-Off desalting.
For DMT-Off DNA:
- Reconstitute a fully deprotected, DMT-Off, dried down oligonucleotide in 2.0mL 0.1M TEAA.
- Load the solution on a properly prepared Glen-Pak DNA cartridge.
- Rinse with 2.0mL 0.1M TEAA.
- Rinse with 2.0mL water.
- Elute in 10% Acetonitrile in water.
- For DMT-Off RNA:
- Conduct standard base deprotection and 2' de-silylation in DMSO and TEA.3HF as recommended in our current TBDMS and TOM Technical bulletins.
- Quench the reaction with 1.75mL RNA Quenching Buffer (60-4120-xx).
Load the resultant 2mL directly on a properly prepared Glen-Pak DNA cartridge
- Rinse with 2.0mL 0.1M TEAA (Fresh 2.0M TEAA diluted in RNase free water).
- Rinse with 2.0mL RNase free water.
- Elute the desalted product in 10% Acetonitrile in RNase free water instead of the standard 30% Acetonitrile/ Ammonium Bicarbonate solution currently recommended for DMT-ON purification of RNA.
In both cases described above, the elution buffer containing 10% Acetonitrile allows for full removal of the DMT-Off oligo, while leaving behind organics, such as benzamide, on the column matrix.
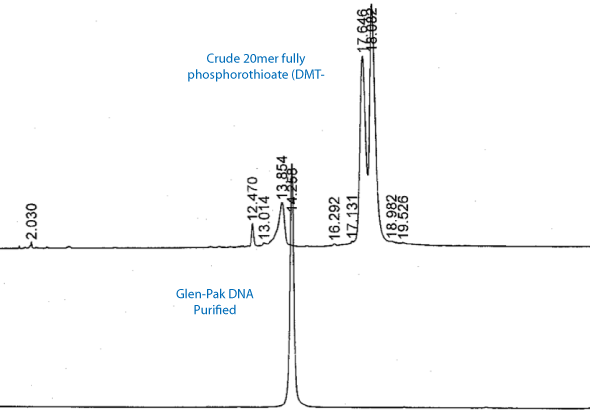
Glen-Pak Phosphorothioate DNA Purification:
The Glen-Pak DNA cartridge may also be used to purify phosphorothioates (S-Oligos) with only some minor changes to the existing DMT-ON method for standard oligonucleotides. The extra hydrophobicity conferred by the addition of sulfur to the oligonucleotide backbone requires both a higher concentration of acetonitrile in the standard salt wash step (12%) to remove the DMT-Off failure products as well as a stronger acid (4% TFA, 60-4042-57) for efficient removal of the DMT prior to elution (See Figure 1).
Glen-Pak DNA Purification of Cy5/5.5 oligos containing dye degradation products:
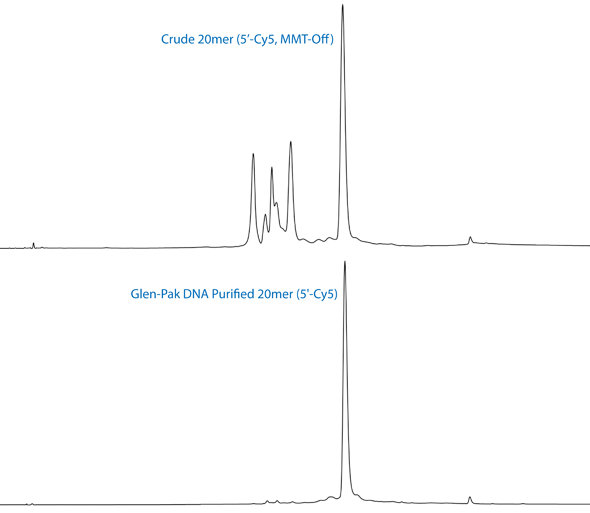
We routinely recommend the use of UltraMild phosphoramidites when synthesizing oligonucleotides containing Cy5 and Cy5.5, as the dye is very sensitive to the ammonium hydroxide and heat normally utilized in deprotection. However, other sequence/chemistry requirements sometimes dictate the use of concentrated ammonium hydroxide at room temperature that leads to the production of a yellow chromophore, which is the degradation product of Cy5 and Cy5.5. One can tell significant degradation has occurred when the solution goes from a clear blue color to turquoise or green.
A twenty base oligonucleotide containing a 5' Cy5 was synthesized MMT-Off and deprotected for 17 hours at 55 °C in concentrated ammonium hydroxide. These conditions were chosen to generate an oligonucleotide that was partially degraded. The deprotected oligonucleotide was dried down, reconstituted in 2.0mL 0.1M TEAA and loaded on a properly prepared Glen-Pak DNA cartridge. This was followed by rinses with 2mL 0.1M TEAA, 2mL 16% Acetonitrile/ 0.1 M TEAA and an elution from the cartridge in 50% Acetonitrile/Water containing 0.5% Ammonium Hydroxide. As seen in Figure 2, the protocol removes failure sequences AND separates the Cy5 degradation product from the intact dye, so the eluted oligo is again a clear blue color. The accompanying spectra for each of the product peaks confirm removal of the degraded Cy5 dye.
Glen-Pak is a trademark of Glen Research Corporation
Product Information
- Glen Report 22.11: Simple Oligonucleotide Modification using Click Chemistry
- Glen Report 22.12: The copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC)
- Glen Report 22.13: tC, tCo and tCnitro: Tricyclic Cytosine Probes of DNA and RNA Structure
- Glen Report 22.14: Saccharin 1-Methylimidazole - An Activator for DNA and RNA Synthesis
- Glen Report 22.15: New Product - A dG Amino-Modifier with Improved Hybridization Characteristics
- Glen Report 22.16:; New Products – α-Tocopherol-TEG Phosphoramidite and 3'-Thiol-Modifier 6 S-S CPG
- Glen Report 22.17: New Products - 8-Oxo-G Clamp and 5'-Amino-Modifier TEG CE Phosphoramidites
- Glen Report 22.18: Deprotection – Volume 4 – Alternatives to Ammonium Hydroxide
- Glen Report 22.19: Technical Brief - Depurination
- Glen Report 22.110: Glen-Pak™ Product Update: New Protocols for Desalting and Purification