Glen Report 8.14: 3'-Terminators
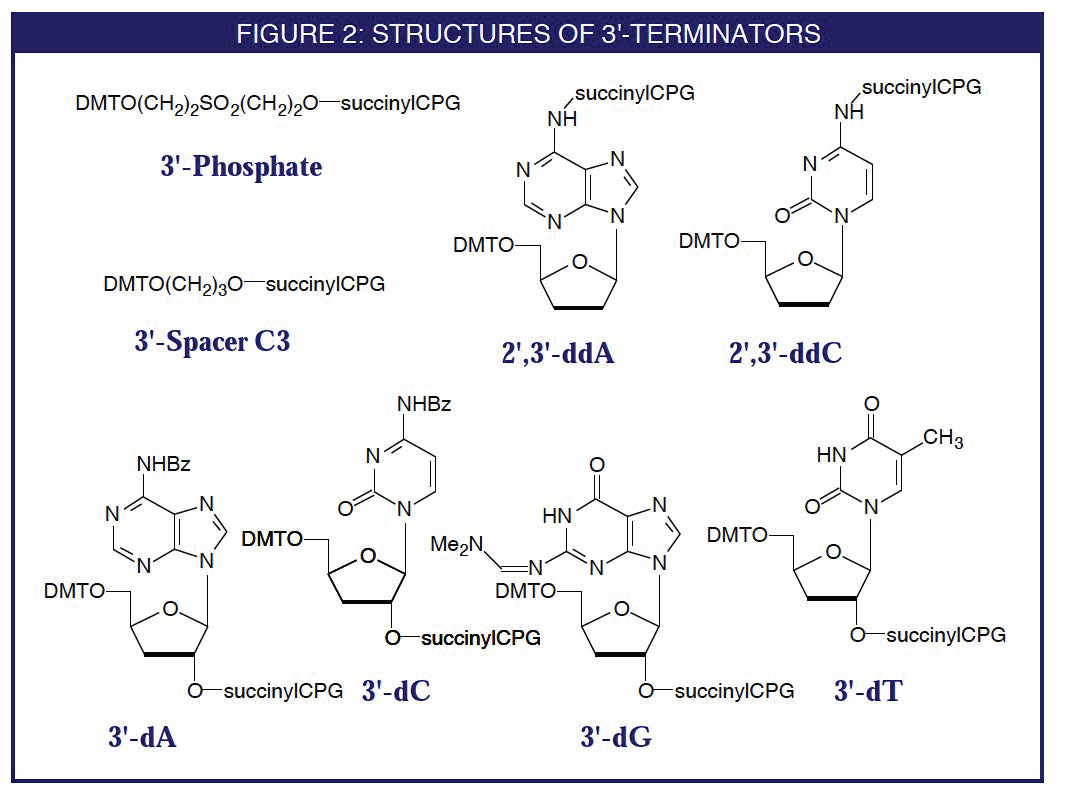
Some sequencing strategies as well as PCR probes require the 3'- terminus of an oligonucleotide to be blocked from allowing polymerase extension. This may be achieved by modifying the 3'-terminus with a phosphate group, a phosphate ester, or using an inverted 3'-3' linkage. However, side reactions during deprotection of the oligonucleotide or enzymatic impurities may free the 3'-hydroxyl group to a small extent. So far, the 3'-propyl phosphate formed using 3'-Spacer C3 CPG has proved to be the simplest and most effective non-nucleosidic blocker of the 3'-terminus.
2',3'-Dideoxynucleosides
The surest way to guarantee blocking the 3'-terminus is using a 2',3'-dideoxynucleoside support. Unfortunately, only ddA and ddC are amenable to attachment to the support through the exocyclic amino group. Both of these supports are now available.
NOTE: ddA is no longer available.
3'-Deoxynucleosides
In situations where it is necessary to have a selection of all four bases available, it is possible to use the 3'-deoxynucleoside supports as 3'-terminators. Although the 2'-hydroxyl group is still present in the final oligonucleotides, it is not a substrate for at least the routinely used polymerases. All four 3'-deoxynucleoside supports will shortly be available, along with their phosphoramidite counterparts.
Product Information
3'-Phosphate CPG (20-2900)
3'-Spacer C3 CPG (20-2913)
2',3'-ddC-CPG (20-2017)
3'-dA-CPG (20-2004)
2',3'-ddA-CPG (20-2007) has been discontinued.
3'-dC-CPG (20-2064)
3'-dG-CPG (20-2074)
3'-dT-CPG (20-2084)