Glen Report 11.12: Oligo Affinity Supports
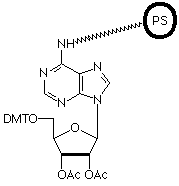
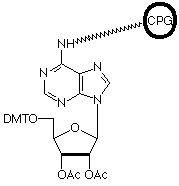
More than eight years ago, we introduced an oligo affinity support (OAS)1 which allowed normal oligonucleotide synthesis but on treatment with ammonium hydroxide, the fully-deprotected oligonucleotide remained attached to the support. After annealing the complementary strand to the support-bound oligonucleotide, an affinity support for the purification of DNA binding proteins was generated.2,3 Unfortunately, the process used to make the support proved to be hazardous and we had to discontinue the product.
In the meantime, highly effective affinity supports could still be prepared by a two-step process in which the oligonucleotide is amino-modified and reacted with a suitable activated support.4,5 However, we have remained intrigued by the elegance of direct production of the support and we continued evaluating potential supports. The criteria for a successful affinity support are simple:
- The support must allow high quality oligonucleotide synthesis using organic solvents.
- The support must also be suitable for use in the aqueous medium of affinity chromatography.
- The support must exhibit low non-specific binding of the intended affinity target.
We are now happy to offer an oligo-affinity polymeric support (PS), designed primarily for affinity purification of biomolecules, and controlled pore glass (CPG), which is less suitable for purification of proteins but ideal for chromatographic applications.
While these supports may find immediate use in the preparation of affinity matrices, we also envisage other potential applications, including enzymatic reactions with ligase and kinase. Also, synthesis in the 5' to 3' sense with 5'-phosphoramidites would yield a supported oligonucleotide with the 3'-terminus available for extension with polymerases.
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
Synthesize the oligonucleotide using standard cycles. (The 3'-base should be entered into the synthesizer as A but it is non-coding. The real 3'-terminal nucleoside is the first monomer added.)
Deprotection
Treat OAS PS with ammonium hydroxide or other deprotecting solutions as normal. OAS CPG can be deprotected with ammonium hydroxide at elevated temperatures but stronger bases may damage the silica structure of the support. In either case, decant or pipet the liquid from the support and wash the support with water until neutral pH is achieved. DO NOT DISCARD THE SUPPORT. The support can be air-dried for storage but it should not be lyophilized.
Cleavage of Oligos from OAS (for Quality Determination)
After synthesis, oligonucleotides are not cleaved from the support by basic media. However, occasionally it may be necessary to cleave the oligonucleotide from the support for anaytical purposes. The attachment to the support is through the N6 position of Adenosine and the oligonucleotide can be cleaved specifically from the support by periodate oxidation followed by ß-elimination yielding the 3'-phosphate.
Periodate Oxidation of the Ribose Ring to the Di-aldehyde
- Treat the support with 1 mL of 100 mM sodium periodate in 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 5-6). If the DMT group is to be retained on the oligonucleotide, adjust the pH to 7.2-7.5.
- Stir or agitate the support in the dark for 6 hours at room temperature.
- Decant or pipet the liquid from the support and wash the support with water (2X2 mL).
ß-Elimination to the 3'-Phosphate
- Prepare solution A by mixing water (2.4 mL), acetonitrile (0.6 mL), and propylamine (0.3 mL)
- Submerge the support in 1 mL of solution A and heat the solution at 50° for 3 hours.
- Decant or pipet the supernatant which now contains the oligonucleotide. Rinse the support with water (2X1 mL) and combine with the supernatant.
- Lyophilize to obtain the product oligonucleotide 3'-phosphate.
References
- Ruth, J., Smith, R.D., Lohrmann, R. Fed. Proc. 1985, 44, 1622.
- C.H. Duncan and S.L. Cavalier, Analytical Biochemistry, 1988, 169, 104.
- J.T. Kadonaga, Methods Enzymol, 1991, 208, 10-23.
- H.C. Kirch, H. Kruger, and H.S. Holthausen, Nucleic Acids Res., 1991, 19, 3156.
- C.L. Larson and G.L. Verdine, Nucleic Acids Res., 1992, 20, 3525.
Product Information
Oligo-Affinity Support CPG (20-4001) has been discontinued.
- Glen Report 11.11: Using Modified Bases to Optimize Hybridization
- Glen Report 11.12: Oligo Affinity Supports
- Glen Report 11.13: New Fluorescent Reagents - TAMRA-dT, Dabcyl-dT
- Glen Report 11.14: The Use of Puromycin CPG in Combinatorial Chemistry
- Glen Report 11.15: Update - Universal Supports, Q-supports
- Glen Report 11.16: More Novel Monomers - 6-Thio-dG, 2'-Amino-RNA, 5-Hydroxy-dC,dU Spacer C18, Spacer 9-CPG